Blog Details
Wireless vs. LAN Connections: Exploring Security Differences
October 25, 2023
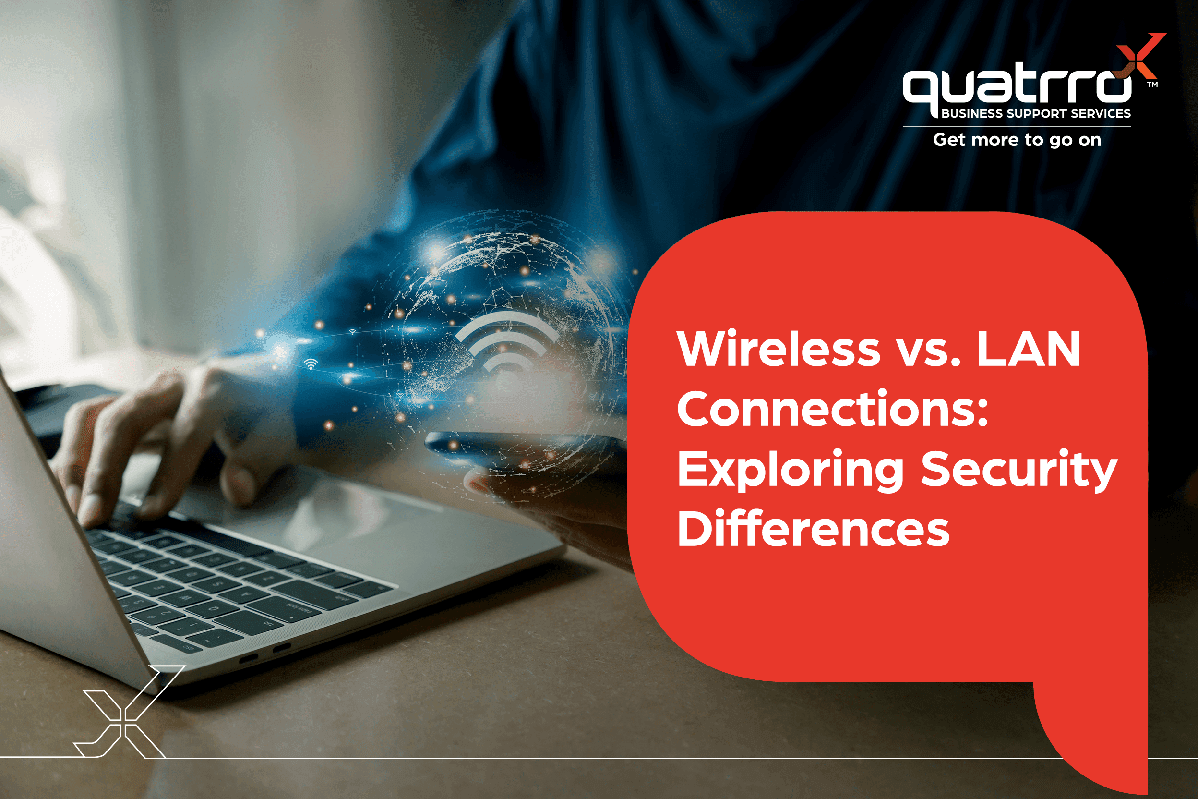
Wireless (Wi-Fi) and LAN (wired) connections, as we all know, are two of the most common ways to connect devices to a network. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages, but the pervading question is which one is more secure.
Wireless connections are frequently regarded as less secure than wired connections. This is due to the fact that the signal travels over the air, where it could be intercepted by unauthorized devices. Additionally, wireless networks are more prone to interference from other electronic devices.
However, it is crucial to note that wireless connections do not have to be inherently less secure than wired connections. There are a number of security measures that can be taken to protect wireless networks, such as using strong encryption and authentication protocols.
In today's digital world, security is more important than ever. Our networks contain a wealth of sensitive data, including personal information, financial data, and business secrets. If this data falls into the wrong hands, it can have significant consequences.
Let’s explore more about Wireless & LAN connections along with their security differences, risks or concerns involved and how to mitigate them.
Understanding Wireless Internet Connections
Wireless internet connections, usually known as Wi-Fi, are a type of network connection that transmits data via radio waves. Wi-Fi is a convenient and pervasive technology that is used in a wide range of devices and applications. However, it is critical to understand the potential security risks associated with utilizing a wireless connection.
Fundamentals of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi networks use radio waves to transmit data between devices and a wireless router. The wireless router is connected to the internet and acts as a gateway for all of the devices on the network to access the internet.
Wi-Fi networks operate on two different frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band is slower but has better range than the 5 GHz band. The 5 GHz band is faster but has a shorter range than the 2.4 GHz band.
Most Wi-Fi devices support both frequency bands. The device will automatically connect to the frequency band that provides the best performance.
Devices and Scenarios Where Wi-Fi is Used
Wi-Fi is used in a wide range of devices and scenarios. Some common examples include:
Smartphones
Tablets
Laptops
Desktop computers
Smart TVs
Streaming devices
Gaming consoles
Smart home devices
Wi-Fi is also used in a wide range of scenarios, including:
Working from home
Online gaming
Streaming movies and TV shows
Browsing the internet
Checking email
Using social media
Shopping online
Banking online
Security Risks Associated with Wireless Connections
The fact that Wi-Fi signals travel through the air is one of the most serious security risks. This means that anyone in the vicinity of your Wi-Fi network has the potential to intercept your data.
Another security concern is that wireless networks are frequently not well-configured and therefore less secure than LAN networks. This makes them easier to target for attackers.
Wired LAN Connections
Wired LAN (local area network) connections are physical links between devices on a network. They are typically made using Ethernet cables, which are plugged into Ethernet ports on the devices. Wired LAN connections are commonly used in businesses and homes to connect devices to the internet and to each other. They are also used in data centers and other high-performance computing environments.
Wired LAN connections are perceived to be more secure than wireless connections because they are not susceptible to eavesdropping or interference. However, they can be more difficult to set up and manage than wireless connections.
Security Advantages of Wired LAN Connections
Wired LAN connections have a number of security advantages over wireless connections, including:
Reduced risk of eavesdropping: Eavesdropping, or the unauthorized interception of data, is not possible with wired LAN connections. This is due to the fact that the data is transferred across a physical cable that cannot be intercepted without physically accessing that wire.
Reduced risk of interference: Wired LAN connections are also less susceptible to interference from other devices. This is due to the fact that data is transmitted over a dedicated cable that is not unknowingly shared with other devices.
Improved security features: Wired LAN networks can also be outfitted with security features like firewalls and intrusion detection systems. These features can aid in the protection of the network from unauthorized access and attacks.
Physical connections are more difficult to intercept: Because wireless signals travel over the air, they are more easily intercepted by unauthorized users. Wired LAN connections, on the other hand, necessitate a physical connection to the network. This makes it more difficult for attackers to gain access to the network and intercept sensitive data.
Wired LAN connections are more reliable than wireless connections: This is due to the fact that they are unaffected by external conditions like interference from other devices or distance from the router.
Disadvantages of Wired LAN Connections
While wired LAN connections have a number of security advantages, they also have some disadvantages, including:
Wired LAN connections can be more difficult to set up and manage. Wireless LAN connections are relatively easy to set up and manage. Wired LAN connections, on the other hand, can be more complex to set up and manage, especially for large networks.
Wired LAN connections can be less convenient. Wireless LAN connections allow users to move around freely while still being connected to the network. Wired LAN connections, on the other hand, require users to be physically connected to the network. This can be less convenient for users who need to move around frequently.
LAN connections are commonly used in a variety of settings, including:
Businesses: Businesses use LAN connections to connect their computers, printers, and other devices to the internet and to each other. This allows employees to share files, access shared resources, and collaborate on projects.
Homes: Homes use LAN connections to connect their computers, smartphones, tablets, and other devices to the internet and to each other. This allows family members to share files, access shared resources, and stream media content.
Schools: Schools use LAN connections to connect their computers, printers, and other devices to the internet and to each other. This allows students to access educational resources, collaborate on projects, and take online tests.
Hospitals: Hospitals use LAN connections to connect their computers, medical devices, and other equipment to the internet and to each other. This allows healthcare professionals to access patient records, share medical images, and collaborate on patient care.
Data centers: Data centers use LAN connections to connect their servers, storage devices, and other equipment to each other. This allows data centers to process and store large amounts of data efficiently.
Potential Security Concerns with Wireless Connections
Here are some of the common security vulnerabilities associated with Wi-Fi networks:
Unauthorized access: Hackers can gain access to a wireless network by compromising the network password or exploiting vulnerabilities in the network router or firmware.
Weak or default passwords: Many users use weak or default passwords for their wireless networks, making them easier to crack for attackers.
Disabled encryption: To enhance performance, some people disable encryption on their Wi-Fi networks. However, this opens the door for attackers to intercept traffic on the network.
Open networks: Open networks are Wi-Fi networks that do not require a password to connect. This type of network is particularly vulnerable to attack, as anyone within range can connect to it.
Outdated firmware: Firmware updates for wireless routers that incorporate security fixes are common. Many individuals, however, do not install firmware updates on their routers. As a result, their networks may be subject to known security flaws.
Misconfigured routers: Wireless routers can be misconfigured in a number of ways that can make them vulnerable to attack. For example, some routers may have ports that are unnecessarily left open or may have weak encryption enabled.
SSID broadcasting: When you enable SSID broadcasting, the name of your Wi-Fi network is transmitted to everyone within range. This makes it simple for attackers to find and target your network.
How Can Hackers Gain Access to a Wireless Network?
Hackers can gain access to a wireless network in a number of ways, including:
Brute-force attacks: A brute-force attack includes attempting a very large number of passwords until the correct one is discovered. This form of attack can be effective against weak or default passwords.
Dictionary attacks: A dictionary attack involves trying a list of common passwords until the correct one is found. This type of attack is also effective against weak or default passwords.
Phishing attacks: A phishing attack entail duping the victim into disclosing their password. For example, an attacker might send a fake email to the victim that appears to be from their internet service provider (ISP). The email might contain a link to a fake website that looks like the ISP's website. If the victim enters their password on the fake website, the attacker will be able to steal it and use it.
Exploiting security vulnerabilities: Hackers can potentially gain network access by exploiting security flaws in wireless routers. An attacker, for example, may uncover a weakness in the router's firmware that allows them to execute code on the router. This code might then be used to steal the router's password or obtain access to network-connected devices.

How Can You Protect Your Wireless Network from Hackers?
There are a number of things you can do to protect your wireless network from hackers, including:
Use a strong password: Use a strong password for your Wi-Fi network that is at least 12 characters long and includes a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Enable encryption: Enable encryption on your wireless router. This will encrypt the data that is transmitted over the network, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept.
Disable SSID broadcasting: Disable SSID broadcasting to prevent your network from being easily identified by attackers.
Keep firmware up to date: Install firmware updates for your wireless router as soon as they are available. This will help to patch any known security vulnerabilities.
Use a firewall: A firewall can help to protect your network from unauthorized access. Most wireless routers have a built-in firewall. However, you may also want to consider installing a firewall on your computer or other devices.
Be careful about what networks you connect to: Only connect to wireless networks that you trust. Avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN.

Security Measures for Wired LAN Connections
While LAN connections are more secure than wireless connections, there are still a number of security measures that can be taken to protect them, including:
Use strong passwords: All devices on the network should have strong passwords.
Enable encryption: Enable encryption on your wireless router. This will encrypt the data that is transmitted over the network, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept.
Enable encryption: Encryption should be enabled on all devices on the network to protect data from being intercepted.
Implementing network segmentation: Network segmentation divides the network into smaller subnets. This can help to contain the damage if a subnet is compromised.
Using a firewall: A firewall can help to protect the network from unauthorized access.
Using intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS): An IDS/IPS can help to detect and prevent malicious activity on the network.
Keeping firmware up to date: Firmware updates for all devices on the network should be installed as soon as they are available.
Create a guest network for visitors. This will help to keep your main network more secure.
In addition to the security advantages listed above, wired LAN connections also offer the following benefits:
Reduced interference: Wired LAN connections are less susceptible to interference from other devices or environmental factors than wireless connections. This can lead to improved performance and reliability.
Centralized management: Wired LAN connections can be centrally managed, making it easier to deploy and maintain security policies.
Scalability: Wired LAN connections can be easily scaled to support a large number of devices and users.
Balancing Security and Convenience
There is a trade-off between security and convenience when selecting a network type. LAN connections are more secure, but often inconvenient. Wireless connections are less secure, but they are more handy in this age of connected technology. The appropriate network type for you will be determined by your specific demands and requirements. If security is of the utmost importance, LAN connections are the better choice. Wireless connections, on the other hand, may be considered if convenience is more essential to you.
Modern Wi-Fi Security Technologies
In recent years, there have been a number of advancements in Wi-Fi security. These advancements have helped to address some of the historical vulnerabilities associated with Wi-Fi.
WPA3
WPA3 is the latest and most secure encryption protocol for wireless networks. It uses a number of advanced security features to protect data from being intercepted and to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the network.
One of the key features of WPA3 is that it uses Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE). SAE is a new handshake protocol that is more resistant to attack than the previous handshake protocol, WPA2-Personal.
WPA3 also includes a number of other security features, such as:
Improved protection against brute-force attacks
Enhanced protection against denial-of-service attacks
Improved security for IoT devices

Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 is the latest generation of Wi-Fi technology. It offers a number of improvements over previous Wi-Fi generations, including faster speeds, better performance in crowded environments, and improved security.
One of the key security features of Wi-Fi 6 is that it uses WPA3 encryption. WPA3 is the most secure encryption protocol available and it offers a number of advanced security features.
In addition to WPA3 encryption, Wi-Fi 6 also includes a number of other security features, such as:
Target Wake Time (TWT): TWT allows devices to negotiate when they will wake up to receive data. This can help to save battery life and improve security.
Protected Management Frames (PMF): PMF encrypts management frames, which can help to protect against certain types of attacks.
Opportunity Network Access (ONA): ONA allows devices to connect to each other directly without the need for a Wi-Fi access point. This can be useful in situations where there is no Wi-Fi access point available or where the Wi-Fi access point is unreliable.
Addressing historical vulnerabilities
Modern Wi-Fi security technologies, such as WPA3 and Wi-Fi 6, address many of the historical vulnerabilities associated with wireless networks. For example, WPA3 provides stronger encryption and protection against password attacks. Wi-Fi 6 also includes a number of security features that protect the Wi-Fi management plane from attack.
Updating Wi-Fi equipment for enhanced security
One of the best ways to improve the security of your Wi-Fi network is to update your Wi-Fi equipment. Many older Wi-Fi devices do not support WPA3 encryption or other modern security features.
If you have an older Wi-Fi router, consider upgrading to a new router that supports WPA3 and other modern security features. You should also make sure that all of your wireless devices are running the latest firmware.
Conclusion
Wireless and LAN connections offers different advantages and disadvantages in terms of security. While wireless connections are more convenient, they are also more susceptible to attack. LAN connections are more secure, but they can be less convenient.
The best type of connection for you will depend on your individual needs and requirements. If security is a top priority, LAN connections are the better choice. However, wireless connections offer a number of other advantages, such as convenience and mobility.
If you do choose to use a wireless network, there are a number of things you can do to improve its security, such as:
Using strong passwords
Enabling encryption
Disabling SSID broadcasting
Keeping firmware up to date
Using a firewall
Here are some additional tips for choosing and securing your network:
Consider your needs and requirements . What is most important to you: security, convenience, or both.
Choose the right type of connection for your needs. If security is a top priority, LAN connections are the better choice. However, wireless connections offer a number of other advantages, such as convenience and mobility.
Take steps to secure your network. Once you have chosen a network type, there are a number of things you can do to improve its security, such as using strong passwords, enabling encryption, and keeping firmware up to date.

In today's digital world, it is more important than ever to secure your wireless network. Wireless networks are convenient and universal, but they are also vulnerable to attack. By following the best practices outlined here, you can help to mitigate the security risks associated with wireless connections and protect your data from unauthorized access.
Here are some tips to keep in mind:
Assess and improve the security of your wireless network. Use the tips in this blog to assess the security of your wireless network and identify any areas for improvement.
Learn more about wireless security and how to protect your network. There are a number of resources available online that can teach you more about wireless security and how to protect your network.
Stay up-to-date on the latest security threats and solutions. Security threats are constantly evolving, so it is important to stay up-to-date on the latest threats and solutions. You can do this by reading security blogs and articles, and by subscribing to security alerts from trusted sources.
Implement the best practices for securing wireless connections. Be sure to implement identified best practices to protect your network from attack.
Seek professional assistance for network security assessments. If you need help assessing the security of your wireless network or implementing security best practices, consider seeking professional assistance from a qualified network security consultant.
Check out these blogs on our subsidiary’s website that talks more about wireless vs. LAN connections
Secure Your Wireless Network And Protect Your Business!5 Tips for Optimizing Your Wireless Networks